In a world crying out for clean, renewable energy, solar energy has emerged as one of the most promising solutions on the horizon.
The Sun showers down a limitless quantity of energy every day, sufficient to power electricity for the whole world multiple times over, if we are able to capture it in an efficient manner. That is exactly what photovoltaic (PV) solar panels are designed to do.
How Solar Panels Generate Electricity from Sunlight?
No need to worry about the answer! We will talk about the complete solar power generation from photons in sunlight and the electricity in homes and industries.
Also, you will find that the answer lies in a fascinating scientific process that converts sunlight directly into electrical energy, a transformation that is both clean and sustainable.
So, let’s get started with the basics of solar energy and photos.
Basics of Solar Energy and Photons - Sunlight to Electricity Conversion
Each beam of sunlight that hits the Earth brings energy in the form of photons, small bundles of light energy. These photons power the conversion of sunlight to electricity conversion.
When photons hit a proper material, they can transfer their energy to electrons within the material, creating the potential for electricity to be generated.
Solar energy is free, abundant, and renewable. The problem is how to tap it efficiently. PV solar panels are designed to receive the energy of photons and convert it into electric current with the help of accurate materials and mechanisms.
The Photovoltaic (PV) Effect: Central Mechanism
The essence of the way solar panels produce electricity is in what scientists refer to as the photovoltaic (PV) effect. This is the underlying physical mechanism by which light is converted into electricity.

When the sun shines on a PV cell, the photons collide with atoms in a semiconductor material, usually silicon. These collisions energise the electrons, releasing them from their atomic bonds. The liberated electrons and the vacant spaces they left behind.
To prevent these electrons from recombining with holes, the PV cell creates an electric field that pushes the electrons in a single direction. This movement of electrons forms an electric current, which is the first step in generating usable solar power and explains how solar panels generate electricity.
Structure of a PV Cell
A single PV cell is the building block of solar panels. Each cell is made primarily from two layers of silicon, one n-type (negatively charged) and one p-type (positively charged).
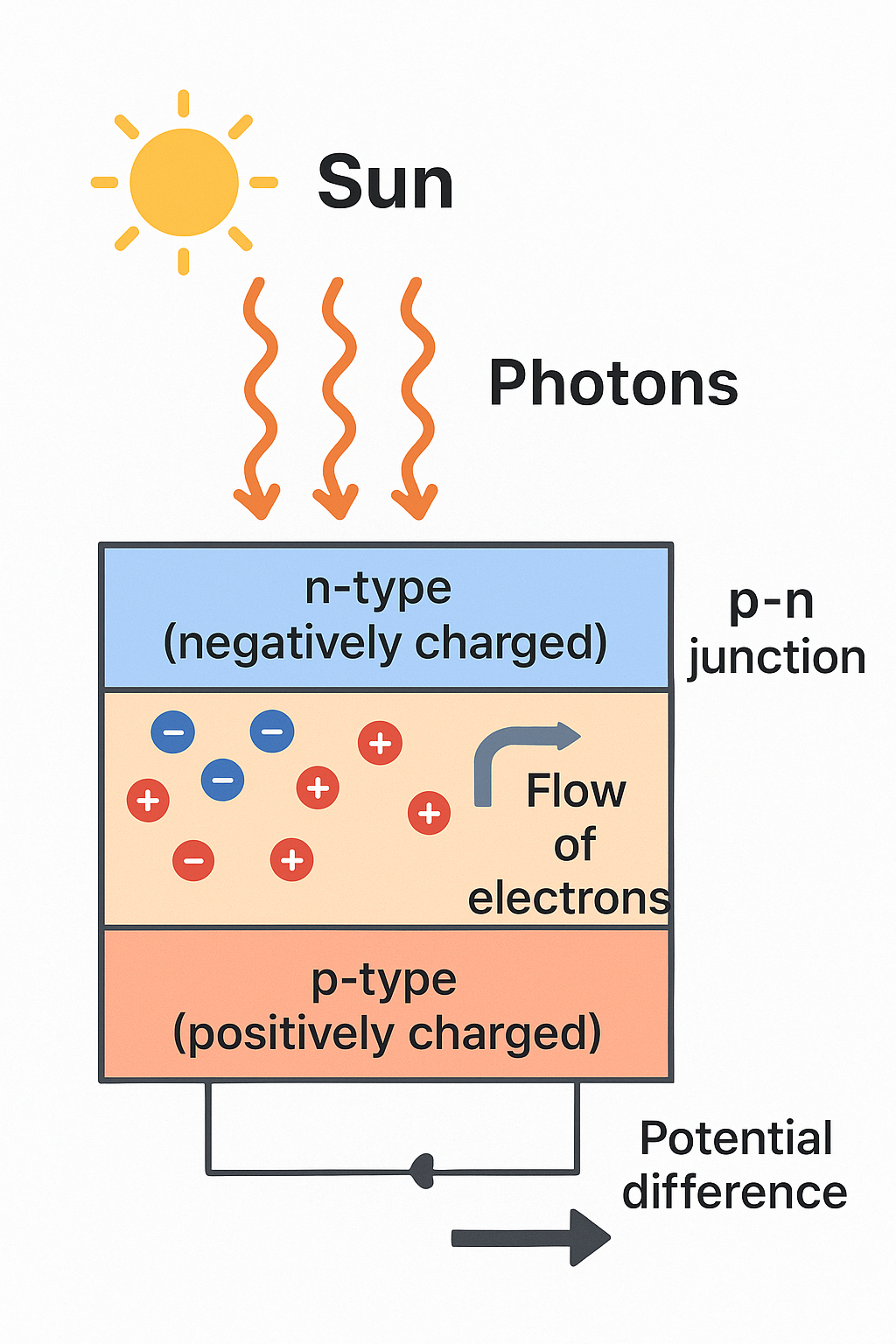 The junction where these two layers meet is called the p-n junction, and it’s here that the magic happens.
The junction where these two layers meet is called the p-n junction, and it’s here that the magic happens.
When the Sun's photons hit the surface, the electrons are energised and begin to move. The p-n junction electric field forces the electrons to one side and holes to the other.
This separation creates a unidirectional flow of the electrons, resulting in a potential difference and contributes to how solar panels generate electricity from sunlight.
Generation of Electric Current
Once the electrons are charged and moving, the next step is to tap into and utilise that movement as electricity. Thin metal contacts on the surface and back of every PV cell provide the pathway for the electrons to move through an external circuit.
As the electrons travel through this circuit, they create direct current (DC) electricity. This DC power can be stored in batteries or passed to an inverter for further treatment.
This movement, powered solely by sunlight, is the essence of the sunlight to electricity conversion process. It's what enables Solar PV systems to generate electricity quietly, without fuel, and without emissions.
Solar Panels' and Modules' Role
While a single Solar PV cell produces relatively low amounts of power, several cells are put together to make a solar panel. Scores of these panels are then wired in arrays to create higher currents and voltages needed for homes, businesses, and industries.
Each panel is constructed with shielding elements like tempered glass, aluminum frame, and junction boxes that protect the cells against environmental degradation such as rain, dust, and hot weather.
Emmvee make sure every solar module is made to function under extreme conditions yet has high efficiency and long lifespan Solar Power Generation Process: From DC to AC
The electricity produced by PV cells is in the form of direct current (DC), while most electrical appliances and grids use alternating current (AC).

So one important part of the solar power generation process is the conversion from DC to AC in a device known as an inverter.
The inverter synchronizes to the grid frequency and supplies the current smoothly, making it compatible with common household and industrial systems.
Recent inverters also have intelligent features like performance monitoring, voltage control, and fault detection to guarantee safe and efficient operation.
Through this conversion, the Sun's power is now usability-ready to illuminate homes, power machinery, and charge gadgets.
System Integration and Usage
After being converted, electricity from the inverter is fed into the distribution panel (or consumer unit), from where it can be utilized to power fans, lights, and other electric appliances.
If your solar system produces more electricity than you use, the excess can be stored in batteries for future consumption or sold to the power grid via a net metering arrangement.
The installation enables you to receive credits for the energy you feed back, helping lower electricity bills and increase sustainability.
Emmvee solar systems are engineered to seamlessly integrate with residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, maximizing output and minimizing maintenance.
From illuminating a rural homestead to energizing a contemporary factory, PV solar panels provide consistent energy where it is most needed.
Factors Affecting Efficiency of Solar Power Generation Process
The efficiency of a solar system varies based on the following factors:
Sunlight intensity and duration: The amount of sunlight translates to the number of photons that hit the panels, which results in higher energy produced. Also, the modern solar systems are designed to work efficiently on cloudy days.
Panel orientation and tilt: When panels are pointed directly at the Sun they can utlise more of its energy throughout the day.
Temperature and conditions: While the temperature can slightly reduce the solar panels, they are designed to perform well across a wide range of weather conditions.
Panel technology: Various solar cell categories, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and bifacial panels, have different levels of efficiency.
Monocrystalline panels, for instance, are famous for being more efficient in conversion, whereas bifacial panels capture light from the rear side as well, thus improving overall output.
Companies like Emmvee keep working on innovative cell designs and material advancements to achieve ultimate conversion efficiency and longevity even in varied Indian climates.
To Wrap up
The trip from the sun to electricity transformation is a stunning illustration of science converging with sustainability. With the photovoltaic effect, the photons of sunlight are converted into electrons that flow, generating clean, renewable energy with no noise or emissions.
With advancing technology, PV systems are becoming more efficient, cost-effective, and accessible, making solar power a viable option for homes, industries, and countries across the globe.
With the top solar innovators such as Emmvee charting the path in design and production, the vision of a solar-powered world is no longer far away.
